To decode treasure maps effectively, you’ll need to understand both historical cartographic elements and modern navigation tools. Focus on interpreting common symbols like cartouches and spiritual markers, while utilizing GPS devices and compass readings to triangulate locations. You must comply with federal and state archaeological regulations, obtain necessary permits, and employ proper safety protocols. The intersection of ancient wisdom and contemporary technology reveals pathways to hidden discoveries.
Key Takeaways
- Treasure maps often combine Spanish and Church codes with natural landmarks, using specific reference points as foundations for location identification.
- Understanding water flow patterns and terrain features like ridges, valleys, and saddles is crucial for navigating treasure map locations.
- Historical maps use cartouches, pictorial signs, and symbolic elements that require contextual interpretation to decode navigational markers.
- Proper authentication involves map forensics, watermark analysis, and ink testing, along with cross-referencing historical documents for legitimacy.
- Legal compliance requires permits for public land excavation, while treasure hunting on private property needs landowner permission.
The Evolution of Map-Making Through History
While the earliest maps emerged over five millennia ago from ancient civilizations like Babylon and Greece, these primitive cartographic works focused primarily on local surroundings with symbolic representations rather than accurate scale.
You’ll find that ancient navigation relied heavily on these early charts, which served both practical purposes and territorial claims.
The cartographic evolution accelerated dramatically during the Renaissance, when Ptolemy’s astronomical principles merged with new scientific methods.
You’ll see this transformation reflected in the development of triangulation techniques and Mercator’s revolutionary projection system.
The invention of the printing press around 1440 democratized map access, while copperplate engraving enabled higher quality reproductions.
In the 18th century, the advancement of lithography techniques revolutionized map production by enabling more detailed and colorful cartographic prints.
Ancient Greeks like Anaximander of Miletus made groundbreaking contributions by creating the first known world map depicting Earth as a cylindrical form.
Decoding Ancient Symbols and Markers
When studying historical maps, you’ll encounter common symbols like cartouches indicating royal names and pictorial signs representing natural landmarks or constructed features.
You’ll need to understand how these symbols often combined phonetic and ideographic elements, requiring contextual interpretation alongside any accompanying text.
Through comparative analysis with known languages and modern imaging techniques, you can now decode many ancient markers that once guided expeditions and marked significant locations.
Egyptian hieroglyphics were initially misinterpreted as purely symbolic until scholars proved they represented sounds and meanings.
Similar to the Rosetta Stone discovery, bilingual texts have proven invaluable for understanding and translating ancient map symbols.
Common Historical Map Symbols
Throughout history, treasure map creators developed intricate systems of symbols to encode essential information about cache locations, religious significance, and navigational markers.
You’ll find spiritual symbolism like the number 3 representing the Holy Trinity, while directional cues utilize compass degrees and geometric relationships. Storage indicators appear as squared U-shapes marking vaults and shafts, often accompanied by sentinel symbols. Since no universal code exists for interpreting treasure maps, symbol meanings often vary by region and historical context. Large oversized markers frequently indicate ancient treasure origins.
When decoding these maps, you’ll encounter numerical codes that double values and connect to letters, forming cryptic messages that bridge multiple cultural systems.
The cultural origins of these symbols vary considerably – from Indian journey narratives to Spanish church markers and pirate brotherhood signs. Each tradition employs distinct methods, whether it’s religious crosses marking peaks or owls indicating treasure rooms marked with “M” symbols.
Treasure Location Reference Points
Building upon these historical symbol systems, specific reference points serve as the practical foundation for treasure location identification.
Symbol interpretations blend Spanish and Church codes with natural markers to create sophisticated mapping techniques. Cultural significance emerges through the careful analysis of these layered clues found in historical sites. False surveying techniques like tic-tac-toe patterns can mislead treasure hunters from authentic trails.
When decoding treasure legends, you’ll encounter these critical markers:
- Letter symbols like “M” and “T” indicating cache rooms or measurement points
- Geometric shapes including triangles and hearts providing precise directional bearings
- Natural formations such as bent trees and stone piles marking pathways
- Painted circular patterns on rocks serving as expedition waypoints
This systematic approach combines geographical features with human-made markers, enabling accurate navigation through complex terrain while preserving the secrecy of valuable locations.
Essential Tools for Modern Expeditions
Modern expeditions demand an extensive toolkit of sophisticated equipment across five essential categories: navigation devices, safety gear, technical climbing equipment, camping essentials, and sustenance management systems.
For navigation essentials, you’ll need GPS-enabled devices paired with satellite communicators like the Garmin inReach Mini, ensuring precise tracking and two-way communication in remote areas. Your expedition tools must include altimeter watches for elevation monitoring and traditional map-compass combinations as reliable backups. Remember to pack waterproof matches for reliable fire starting in any conditions.
Don’t forget power banks to maintain device functionality. Technical gear requirements encompass specialized harnesses, carabiners, and climbing helmets, while camping gear focuses on climate-specific tents and sleeping systems. The Black Diamond Momentum harness provides lightweight support for alpine climbing.
Your kit should include thorough first aid supplies, emergency shelters, and ample food and water purification systems to handle unexpected situations.
Understanding Terrain Features and Natural Landmarks
When you’re traversing through potential treasure sites, you’ll need to recognize key landforms like hills, ridges, valleys, saddles, and depressions that often conceal historical caches.
You must interpret water flow patterns by studying draws and drainages, as ancient settlers frequently used these natural features to mark their routes and hiding spots.
Ancient trail markers, including strategically placed rock cairns and modified spurs, can reveal pathways to hidden locations when you understand their relationship to surrounding terrain features. Successful navigation requires detailed seasonal examination since vegetation changes throughout the year can drastically alter the visibility of these features.
Successful navigation through varied terrain relies heavily on understanding and identifying key landforms that serve as natural waypoints and orientation markers.
The landform significance in expedition planning can’t be overstated, as these features form the foundation of reliable navigation strategies.
- Hills stand as prominent elevated points with all-around slopes, providing excellent vantage points and distinct reference markers visible from considerable distances.
- Ridges offer natural elevated pathways with their elongated crests, serving as reliable travel routes while maintaining clear sight lines.
- Valleys create natural corridors between higher ground, often containing water sources and providing protected passage through challenging terrain.
- Saddles present natural mountain passes between elevated features, offering essential interchange points for crossing between different areas.
Reading Water Flow Patterns
Reading water flow patterns on topographic maps requires understanding the intricate relationship between elevation changes and drainage systems. You’ll notice that stream dynamics create distinctive “V” shapes, with the point indicating downstream direction and arms extending toward higher elevations.
Through contour analysis, you can determine flow direction by observing how lines bend uphill across gullies and drains.
When examining watersheds, you’ll find that water consistently moves perpendicular to contour lines, flowing from higher to lower elevations. Perennial streams appear as solid blue lines, while intermittent waterways show broken patterns.
Understanding groundwater flow adds another dimension, as it typically follows hydraulic gradients that align with surface drainage basins. These patterns reveal essential navigation markers and potential water sources for your expedition planning.
Identifying Ancient Trail Markers
Throughout North America’s rich navigational history, trail marker trees served as sophisticated living signposts, carefully engineered by Native American tribes and early settlers to indicate critical resources and pathways.
When seeking authentic trail marker identification, you’ll find these culturally significant guides most prevalent in the eastern and southern United States, particularly along indigenous routes.
To verify a genuine trail marker tree’s authenticity, look for these distinct characteristics:
- A sharp horizontal bend occurring few feet above ground level
- Vertical growth emerging from the bent portion
- Age exceeding 200 years for Native American origins
- Alignment with historic waterways or settlement sites
You’ll typically discover these modified trees on elevated terrain, where they’ve guided travelers to water sources, safe passages, and sacred grounds for generations.
Legal Considerations and Property Rights
When engaging in treasure hunting activities, you must navigate a complex web of federal and state laws that govern artifact collection and property rights.
You’ll need permits for excavation on public lands under the Archaeological Resources Protection Act, while state laws vary regarding private property discoveries. To avoid legal implications, always secure written agreements with landowners before searching their property.
Property disputes often arise when valuable items are discovered.
You’ll find that artifacts on private land typically belong to the landowner, while those on public lands belong to the government. Native American cultural items must be returned to tribes, and shipwrecks within state waters fall under state jurisdiction.
Safety Protocols for Treasure Hunting
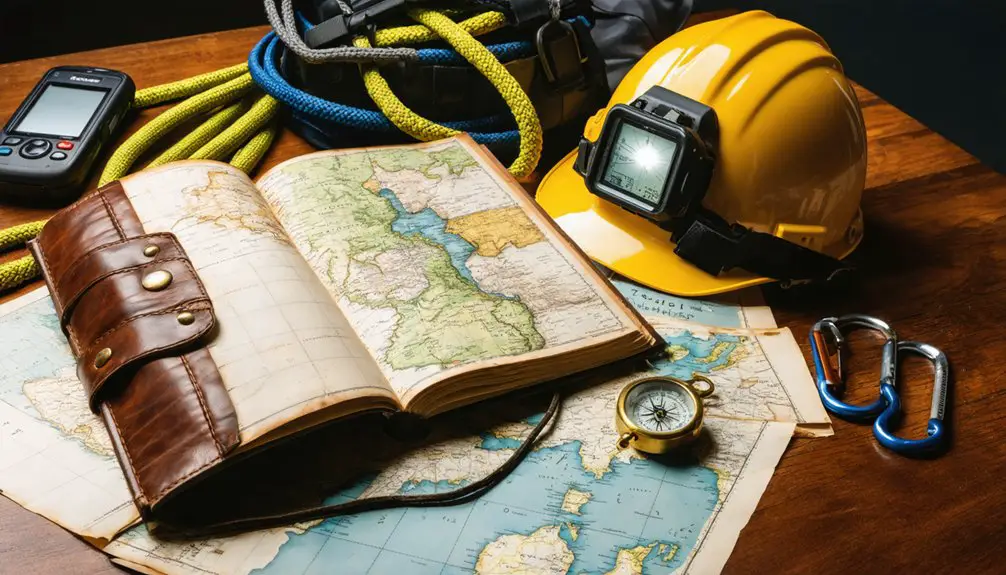

Beyond the legal framework of treasure hunting lies the paramount domain of safety protocols. Your adherence to methodical preparation and risk management practices determines your expedition’s success and survival.
Essential safety gear, including GPS devices and protective clothing, forms your first line of defense against environmental hazards.
- Establish reliable emergency contacts and detailed check-in procedures before venturing into remote locations.
- Equip yourself with terrain-appropriate tools, from metal detectors to wilderness survival equipment.
- Monitor environmental conditions through weather forecasts and wildlife activity patterns.
- Deploy systematic risk assessment protocols for each new search area.
You’ll maximize both safety and discovery potential by maintaining disciplined adherence to these protocols while preserving your freedom to explore promising sites.
You’ll need to master both basic trail markers and precise compass bearings to effectively navigate toward potential treasure locations in varied terrain.
Your compass work must incorporate proper housing alignment with magnetic north while maintaining a steady hand position to follow accurate bearings between waypoints.
When moving through unmarked areas, you’ll combine these navigation methods with careful observation of natural features like ridgelines and waterways to maintain your plotted course.
Trail Markers And Bearings
Trail markers and directional bearings form the foundational elements of successful field navigation during expeditions.
You’ll encounter diverse trail marker types, from painted blazes to cairns, each serving critical navigation safety functions in different terrain conditions. Understanding their placement at eye level and consistent spacing guarantees you’ll maintain proper orientation throughout your journey.
- Watch for bright ribbons and flagging tape that mark wilderness routes
- Identify paint blazes strategically positioned on trees and rocks
- Note wooden signs at intersections providing directional guidance
- Locate cairns marking paths across open, rocky terrain
When traveling between markers, maintain awareness of natural landmarks, drainage patterns, and prominent peaks.
You’ll want to regularly cross-reference these features with your map while tracking the sun’s position and keeping a running tally of passed terrain features.
While mastering compass-based navigation requires methodical practice, the fundamental techniques remain consistent across all field applications.
You’ll need to start with proper compass calibration, accounting for magnetic declination in your region to guarantee navigation accuracy. Regular compass maintenance keeps your readings reliable across varying terrain.
When taking bearings, you’ll want to make precise bearing adjustments based on your terrain assessment. Environmental influences like metal objects or magnetic deposits can affect your compass’s performance, so maintain distance from potential interference.
Different compass types serve various purposes – while basic models work for general navigation, specialized varieties like the Swedish compass offer enhanced precision for detailed work.
You’ll find success by combining these technical aspects with practical field experience, allowing you to navigate confidently through challenging landscapes.
Popular Treasure Map Legends and Stories
Throughout history, treasure maps have captured imaginations and inspired expeditions through their intriguing blend of documented clues and mythological elements.
Pirate legends and treasure folklore continue to drive modern-day quests, from Captain Kidd’s encoded markers at Cliffwood Beach to the mysterious Beale Ciphers of Virginia.
You’ll discover these fascinating historical accounts in documented treasure maps:
- The Copper Scroll’s precise measurements and 63 hidden locations of ancient wealth
- Captain Kidd’s strategic use of twin elm trees called “Kidd’s Rangers” as navigational markers
- The Beale Ciphers’ three encrypted documents pointing to vast riches in gold and silver
- El Dorado’s mythical golden city, which drove numerous expeditions through South America
These enduring mysteries demonstrate how treasure maps blend geographical precision with cryptic symbolism, creating lasting quests for hidden wealth.
Map Authentication and Verification Methods
Since authenticating treasure maps requires rigorous scientific analysis, experts employ an extensive suite of verification methods to distinguish genuine historical documents from sophisticated forgeries.
Through map forensics, you’ll encounter physical examination techniques like watermark analysis and ink composition testing, combined with cutting-edge digital tools for georeferencing and pattern recognition.
Historical cartography experts scrutinize every detail, from paper texture to symbolic elements, while cross-referencing archived documents and expedition logs.
You can rely on chemical testing methods, including spectroscopic analysis and radiocarbon dating, to verify material authenticity.
Modern authentication processes integrate multidisciplinary approaches, combining traditional expertise with advanced technology.
This thorough framework helps you establish the legitimacy of potentially valuable maps through documented provenance and certified expert validation.
Technology Integration in Modern Map Reading
As modern cartography evolves into the digital age, technology integration has revolutionized map reading through interconnected systems of data acquisition and processing.
Geospatial technology has transformed traditional navigation into dynamic, interactive experiences that enhance your expedition planning and execution.
The map evolution continues through these cutting-edge developments:
- LiDAR and drone mapping create precise 3D terrain models, enabling you to analyze potential routes with unprecedented accuracy.
- Real-time data integration delivers current conditions, empowering your decision-making with live weather and terrain updates.
- AI-powered navigation learns your preferences, offering personalized route suggestions tailored to your expedition style.
- Augmented reality overlays project waypoints and critical information directly onto your field of view, maximizing situational awareness.
These advancements guarantee you’ll navigate with greater confidence and precision during your treasure hunting endeavors.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can You Determine if a Treasure Has Already Been Found?
You’ll need to conduct treasure verification through official databases, consult archaeological records, analyze artifact analysis reports, and check historical documentation to determine if someone’s already discovered the treasure.
What Psychological Traits Make Someone More Successful at Decoding Treasure Maps?
You’ll excel at map decoding with strong cognitive flexibility to adapt to unclear clues, heightened pattern recognition abilities to spot hidden symbols, and unwavering persistence to explore unconventional interpretations.
How Do Seasonal Changes Affect the Accuracy of Treasure Map Landmarks?
You’ll find those reliable landmarks aren’t so dependable after all – seasonal visibility transforms vegetation, terrain, and light conditions, greatly altering or obscuring key markers you’re searching for year-round.
Which Historical Figures Were Known for Creating Deliberately Misleading Treasure Maps?
You’ll find little historical evidence of deliberate map deception by pirates. While pirate deception exists in treasure folklore, documented cases are absent. Thomas J. Beale’s ciphers remain the closest example.
How Do Underwater Treasures Affect Traditional Map-Reading Techniques and Symbols?
Like peering through murky glass, you’ll notice underwater symbols require special adaptations. You’re dealing with 3D navigation, depth markers, and visibility-optimized map features to overcome aquatic challenges.
References
- https://goldxtra.com/the-importance-of-maps-to-find-treasure/
- https://ftp.survation.com/how-do-buried-treasure-maps-determine-where/
- https://uoalive.com/wiki/Treasure_Maps
- https://www.treasurenet.com/threads/a-guide-to-vault-treasure-hunting-condensed.519355/
- https://www.lostadamsgold.com/2017/07/09/decoding-treasure-symbols-on-a-map/
- https://www.bimcc.org/history-of-cartography/timelines
- https://www.icsm.gov.au/education/fundamentals-mapping/history-mapping
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_cartography
- https://www.smithsonianmag.com/innovation/brief-history-maps-180963685/
- https://historyguild.org/mapping-the-world-a-short-history-of-cartography/