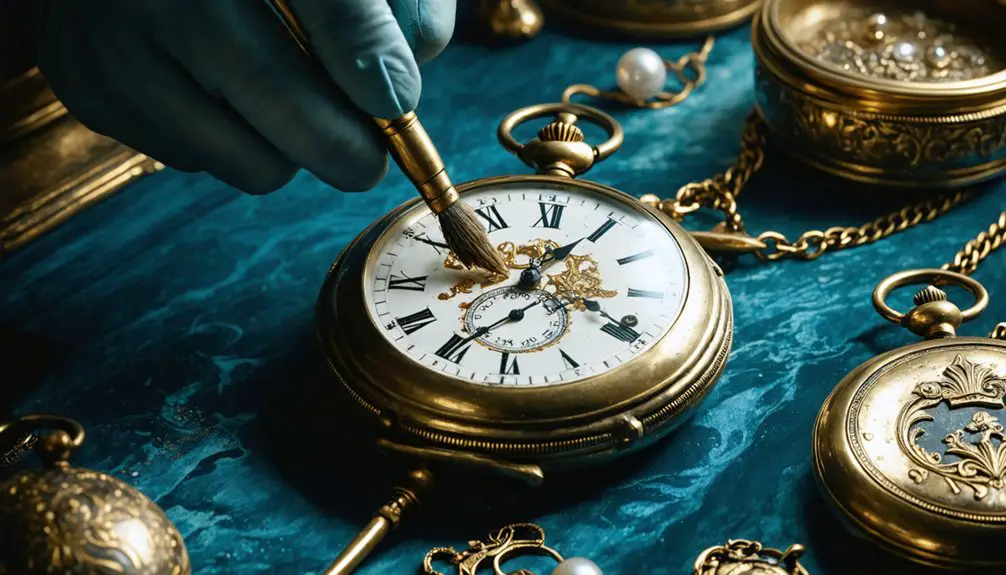
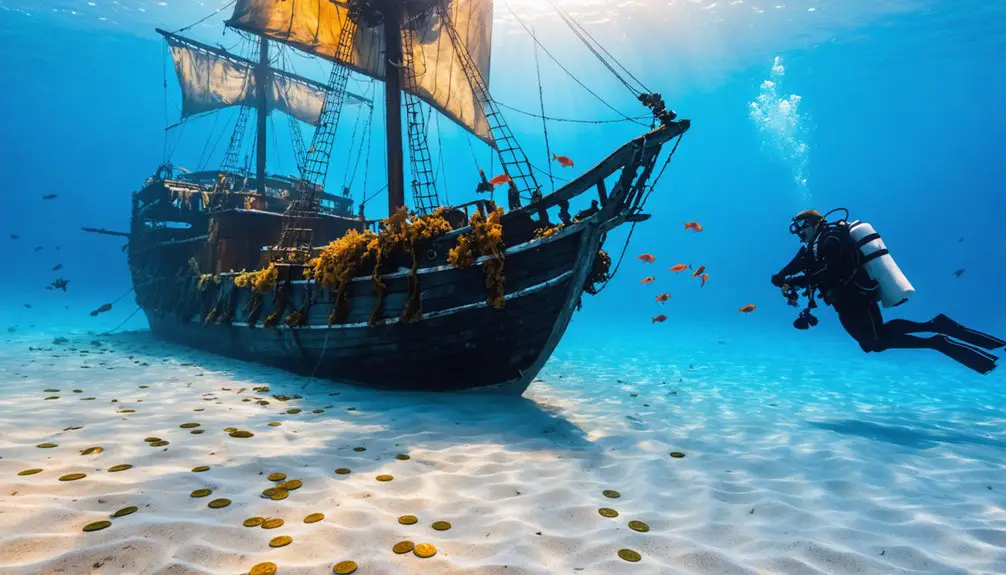
When you recover treasures from sunken ships, you’ll need to act quickly within the first 48 hours to prevent deterioration. Keep artifacts submerged in seawater or specialized solutions while maintaining stable temperatures between 18-22°C. You’ll require different treatments based on material type: PEG for wood, electrolytic reduction for metals, and careful desalination for ceramics. Advanced techniques like 3D scanning and chemical stabilization guarantee proper preservation. The world of maritime conservation holds countless specialized methods to protect these priceless finds.
Key Takeaways
- Keep recovered artifacts submerged in water during the first 48 hours to prevent deterioration and damage from environmental exposure.
- Apply specialized treatments based on material type: electrolytic reduction for metals, PEG for wood, and salt removal for ceramics.
- Document artifacts through high-resolution photography and 3D modeling before beginning any restoration or cleaning procedures.
- Maintain strict temperature and humidity controls during transport and storage, with humidity levels between 40-60% RH.
- Use gentle cleaning methods like soft brushes and controlled desalination processes to remove sediment and stabilize artifacts.
The First 48 Hours: Critical Steps in Artifact Preservation
When marine archaeologists recover artifacts from sunken ships, the first 48 hours prove absolutely vital for preservation.
You’ll need to keep recovered items completely submerged in water to prevent rapid deterioration from oxygen exposure and temperature changes.
During artifact recovery, you’re facing preservation challenges that demand immediate attention – careful documentation and minimal handling are essential. Water pressure and salinity can significantly impact the structural integrity of recovered artifacts.
You’ll want to use gentle tools like soft brushes and plastic implements to remove sediment without damaging delicate surfaces.
Maintaining a stable temperature range between 18-22°C helps prevent further deterioration of sensitive materials.
It’s important to monitor environmental conditions while transporting artifacts to conservation facilities, keeping them either submerged or refrigerated to minimize chemical changes.
For best results, you must begin salt removal procedures promptly using controlled freshwater baths, as salt crystallization can cause irreversible damage if not addressed quickly.
From Ocean Floor to Conservation Lab
You’ll need to act swiftly once artifacts break the ocean’s surface, as exposure to air and changing environments can trigger rapid deterioration of previously stable materials.
Conservation lab safety protocols require you to maintain strict temperature and humidity controls while handling recovered items, particularly when working with unstable metals or waterlogged organic materials.
Your immediate preservation efforts must include keeping specimens consistently wet during transit and implementing appropriate desalination procedures before any detailed cleaning or restoration work begins. Expert salvage teams often employ weight management techniques to carefully transport delicate artifacts from deep waters while maintaining their structural integrity. Modern shipwreck hunters rely on side-scan sonar technology to precisely locate artifacts before beginning any recovery operations.
Immediate Preservation After Recovery
The successful preservation of recovered underwater artifacts hinges on immediate and precise stabilization procedures during transport from the ocean floor to conservation facilities.
When you’re handling artifact recovery, you’ll need to keep waterlogged items consistently wet using seawater or specialized conservation liquids to prevent destructive drying. You’ll want to shield your finds from rapid environmental changes that could trigger warping or cracking. Complex material management requires specialized techniques for different types of artifacts found at shipwreck sites.
Preservation techniques demand meticulous attention to temperature and humidity control during transport. You’ll need to use climate-controlled containers and vehicles while monitoring conditions with data loggers. For wooden artifacts, conservators must apply polyethylene glycol treatment to prevent structural collapse.
It’s crucial to document every detail of the artifact’s origin, position, and condition through photographs and 3D scans. This thorough documentation guarantees you’re maintaining both the physical integrity and historical context of these irreplaceable treasures.
Conservation Lab Safety Protocols
Since safety protocols form the foundation of successful artifact conservation, qualified personnel with specialized training in underwater archaeology must oversee all recovery operations.
You’ll need to guarantee your lab safety measures include proper ventilation systems and fume hoods for chemical handling, while maintaining controlled humidity and temperature levels to protect artifacts.
When you’re working in the conservation lab, you’ll want to separate wet and dry storage areas to prevent cross-contamination.
Don’t forget to use dechlorinated water with chemical inhibitors in storage tanks to prevent corrosion and microbial growth.
You must limit UV exposure to protect organic materials and pigments from degradation.
Remember to document every step of your conservation process, and always wear appropriate protective equipment when handling chemicals or fragile artifacts.
Following professional and ethical standards is essential for maintaining the integrity of underwater archaeological investigations during the conservation process.
Establishing operational inventories of recovered artifacts helps track and manage conservation progress effectively.
Specialized Treatment Methods for Different Materials
Preserving artifacts recovered from underwater sites requires highly specialized treatment methods tailored to each material’s unique characteristics and deterioration patterns.
Proper artifact handling demands meticulous attention to material compatibility and the specific challenges each type faces after prolonged submersion.
You’ll find that metals need electrolytic reduction and protective coatings, while waterlogged organics require PEG treatments and controlled drying.
For ceramics and glass, you’re looking at salt removal through diffusion baths and careful reconstruction with reversible adhesives.
Stone artifacts demand targeted mechanical cleaning and chemical poultices to dissolve stubborn concretions.
Success depends on maintaining precise environmental controls throughout treatment.
You’ll need to monitor temperature, humidity, and salinity levels constantly while documenting every step with advanced imaging techniques.
The team must consider how water pressure and temperature have impacted the artifacts during their time underwater to determine the most effective preservation approach.
Managing Salt Contamination in Retrieved Objects
When you’re managing salt-contaminated artifacts from shipwrecks, you’ll need to begin with controlled desalination baths that match the object’s original salinity before gradually reducing salt levels through systematic water changes.
For metal objects, particularly iron-based artifacts, you’ll want to employ specialized chemical treatments that can safely extract chlorides while preventing further corrosion during the process. This careful treatment is essential since untreated iron objects can deteriorate rapidly when exposed to salt.
Wooden artifacts require careful soaking protocols that balance salt removal with structural preservation, as you must prevent cellular collapse while maintaining the artifact’s dimensional stability throughout the desalination process.
Desalination Bath Best Practices
After recovering artifacts from marine environments, proper desalination becomes critical to prevent ongoing deterioration from chloride ions trapped within the objects.
You’ll need to set up a bath system that allows for complete submersion of artifacts in containers sized to maintain effective salt removal. Start with a controlled mixture of seawater and freshwater to prevent osmotic shock.
To optimize your desalination techniques, monitor conductivity levels regularly and gently stir the bath before taking measurements.
You can enhance the process through mechanical agitation and moderate temperature increases, though you’ll want to avoid excessive heat that could damage delicate materials.
Replace bath water consistently to maintain the concentration gradient driving salt extraction. For fragile items, consider using poultice treatments as an alternative to full immersion.
Chemical Treatments For Metals
Chemical stabilization of marine-recovered metals requires a carefully orchestrated approach combining alkaline solutions and inhibitors.
You’ll need to start with a 1% potassium dichromate solution mixed with sodium hydroxide at pH 9-9.5 for long-term preservation, while temporary stabilization can utilize 5% sodium carbonate solutions. These chemical reactions help control corrosive processes during treatment.
Before addressing preservation challenges, you’ll want to conduct X-ray analysis to assess encrustation composition and determine the metal’s condition. This evaluation guides your treatment strategy.
Don’t remove protective corrosion layers immediately – they act as natural shields. Instead, use electrolytic cleaning with controlled current to remove chlorides systematically.
Monitor conductivity levels throughout treatment to guarantee proper salt removal, and consider applying organic coatings as a final protective barrier against future deterioration.
Wood Preservation Through Soaking
Because waterlogged wood from marine environments contains high levels of destructive salts and sulfur compounds, you’ll need to implement immediate preservation measures through specialized soaking treatments.
The key to successful wood preservation lies in controlling moisture levels while removing harmful substances through systematic soaking procedures.
Essential wood soaking preservation techniques follow this sequence:
- Maintain constant moisture upon recovery to prevent immediate structural collapse
- Begin PEG soaking treatment to replace water molecules within wood’s cellular structure
- Apply neutralizing alkaline solutions to combat acid formation from sulfur oxidation
- Utilize SP-11 treatment in combination with PEG for enhanced stability
These preservation techniques guarantee your recovered wooden artifacts maintain their structural integrity while neutralizing destructive compounds that could otherwise lead to rapid deterioration upon exposure to air.
Advanced Cleaning and Stabilization Techniques
While marine artifacts often arrive in severely degraded states, advanced cleaning and stabilization techniques have revolutionized their restoration.
You’ll need to carefully monitor artifact integrity throughout the desalination process, using conductivity meters to track salt removal. Depending on the material, treatment duration can range from months to over a year.
You can employ electrochemical methods to stabilize metals and remove concretions through controlled hydrogen bubble evolution.
For delicate pieces, you’ll want to use passive diffusion with regular water changes.
X-ray and CAT scans will guide your mechanical cleaning, helping you navigate complex concretions that might hide additional artifacts.
When working with iron objects, electrolytic cleaning in soda ash solutions proves particularly effective at extracting stubborn chlorides while preserving protective corrosion layers.
Documentation and Analysis During Restoration

As marine artifacts emerge from their watery graves, meticulous documentation becomes essential for preserving historical context and guiding restoration decisions.
You’ll need to implement thorough artifact documentation protocols that integrate both traditional and digital techniques during the restoration process.
Key analysis techniques you’ll employ include:
- High-resolution photogrammetry to create detailed 3D models capturing surface details before treatment
- Continuous video recording to document each restoration phase while preserving vital contextual information
- Digital database logging with unique identifiers linking artifacts to their recovery locations and treatment history
- GIS mapping to analyze spatial relationships between artifacts and track their movement through the conservation process
You’ll find these documentation methods critical for maintaining scientific integrity while ensuring future researchers can understand and verify your restoration decisions.
Historical Context and Authentication Process
Understanding the historical context and authentication of recovered marine artifacts represents a crucial foundation for any restoration project.
You’ll need to evaluate the historical significance of shipwrecks like the San José, which sank during major military conflicts and carried valuable cargo that’s now at the center of legal disputes between nations.
When you’re authenticating recovered items, you’ll rely on a thorough approach that combines historical research, scientific analysis, and legal documentation.
You’ll use advanced technologies like XRF and radiocarbon dating to verify age and composition, while matching artifacts to known ship manifests and historical records.
Through multidisciplinary research, you can trace items to specific wrecks by examining cargo types, coin mintings, and ship construction details, ensuring the authenticity of each piece before restoration begins.
Environmental Control Systems for Long-Term Storage
You’ll find that temperature control in artifact storage requires precise regulation through specialized conservation chambers that prevent rapid moisture loss and maintain structural integrity.
Continuous monitoring systems track temperature fluctuations in real-time, allowing you to respond quickly to any deviations that could compromise the artifacts’ stability.
Your humidity control strategy must incorporate both HEPA filtration systems and customized moisture levels to protect different material types, particularly waterlogged objects from marine excavations.
Temperature Control Strategies
When preserving artifacts recovered from sunken ships, maintaining precise temperature control stands as a critical factor in their long-term survival.
Temperature fluctuations can trigger devastating chemical reactions, especially in maritime artifacts with complex salt compositions. You’ll need to understand artifact sensitivity to create ideal storage conditions between 15°C and 20°C.
Modern conservation facilities employ these essential control strategies:
- HVAC systems with digital sensors that detect and respond to temperature variations instantly
- Zoned temperature controls tailored to different material types and their specific needs
- HEPA and activated charcoal filtration systems that maintain thermal balance
- Secondary thermal buffers using phase change materials to prevent sudden temperature swings
You’ll find these measures critical in preventing accelerated degradation while ensuring your recovered treasures remain stable for future generations.
Humidity Monitoring Methods
Proper humidity monitoring forms the cornerstone of preserving maritime artifacts in long-term storage environments.
You’ll need to select from several humidity measurement techniques to maintain ideal conditions between 40-60% RH. Basic humidity indicator strips offer quick, cost-effective readings, while electronic meters provide ±3-5% accuracy with greater convenience.
For thorough monitoring, you’ll want to leverage advanced humidity sensor types like wireless data loggers.
These devices let you track conditions continuously without disturbing artifacts, while cloud connectivity enables real-time alerts and remote access.
When integrated with environmental control systems, these sensors work alongside dehumidifiers to maintain stable conditions. This prevents damaging RH fluctuations that could compromise your artifacts through mold growth, corrosion, or physical stress.
Digital Mapping and 3D Reconstruction
Modern digital mapping and 3D reconstruction technologies have revolutionized the documentation of underwater archaeological sites.
You’ll find these advanced techniques essential for digital preservation, combining multiple data sources to create thorough site records without repeated physical diving.
When you’re exploring underwater archaeology sites, you’ll encounter four key technological approaches:
- Marine magnetometers that detect magnetic field distortions from metal artifacts
- Side-scan sonar systems generating detailed acoustic seafloor imagery
- GPS-integrated photogrammetry capturing high-resolution 3D models
- Digital elevation models combining bathymetric and topographic data
These tools help you overcome challenging underwater conditions while creating precise digital archives.
Advanced digital tools enable archaeologists to document submerged sites with precision, conquering the obstacles of underwater exploration.
You can now virtually explore shipwrecks, monitor site degradation, and plan conservation strategies with unprecedented accuracy, though water turbidity and equipment costs remain limiting factors.
Modern Technologies in Maritime Conservation

As maritime conservation evolves, revolutionary technologies are transforming how you’ll preserve and protect underwater cultural heritage.
You’ll find AI advancements powering underwater robots that extend conservation capabilities beyond human limits, while sustainable practices incorporate solar-electric hybrid engines that slash carbon emissions by 75%.
Conservation robotics now includes autonomous underwater vehicles that gather precise environmental data around wreck sites.
Through underwater monitoring systems, you’ll access real-time data from smart buoys and sensor arrays tracking marine species and water quality.
Eco-friendly technologies, like zero-discharge systems and acoustic innovations, help prevent pollution while monitoring marine mammal populations.
You’ll benefit from predictive analytics and data integration that combine satellite observations with environmental sensors, creating extensive solutions for preserving maritime artifacts while protecting the marine ecosystem they inhabit.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Does It Typically Cost to Restore a Major Shipwreck Artifact?
You’ll need to allocate between $80-100 for initial artifact valuation and processing, plus $3 annually for maintenance, while specialized restoration techniques for metal pieces can extend costs over multiple years.
Can Private Collectors Purchase Restored Artifacts From Historically Significant Shipwrecks?
You can’t legally purchase artifacts from historically significant shipwrecks due to private ownership restrictions and ethical considerations. Most items must remain in public collections for research and preservation purposes.
What Percentage of Recovered Artifacts Survive the Restoration Process?
While survival rates vary dramatically by material type, you’ll find that artifact preservation success ranges from 40-80%. Restoration challenges mean delicate organic materials have much lower survival rates than ceramics or metals.
How Long Do Shipwreck Treasures Typically Maintain Their Value After Restoration?
You’ll find that properly restored shipwreck treasures maintain value for decades, with market demand often driving value appreciation 2-20 times higher than non-salvaged equivalents, especially for precious metals and certified pieces.
Which Countries Currently Lead in Successful Shipwreck Restoration Projects?
Like ancient mariners charting new waters, you’ll find Greece and the United States leading shipwreck regulations through international collaborations, with extensive restoration projects and multi-million dollar ecosystem recovery programs.
References
- https://www.rumtherapy.com/2011/07/searching-for-pieces-of-eight/
- https://divernet.com/scuba-diving/how-to-correctly-excavate-a-shipwreck-2/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marine_salvage
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b24Je-Gm5Ls
- https://www.airbag.cc/three-ways-to-salvage-a-sunken-ship/
- https://turkishmuseums.com/blog/detail/underwater-archaeology-discovery-conservation-and-restoration/10081/4
- http://www.marinebiodiversity.ca/saving-history-below-the-waves-expert-methods-for-preserving-submerged-artifacts/
- https://library.fiveable.me/archaeology-of-the-age-of-exploration/unit-3/conservation-underwater-artifacts/study-guide/wW2vgskMSrN91Cu4
- https://oceanexplorer.noaa.gov/explorations/12newworld/background/underarch/underarch.html
- https://www.history.navy.mil/research/underwater-archaeology/conservation-and-curation/ua-conservation-heritage.html



