When cleaning beach-found metal artifacts, you’ll need to act quickly to prevent salt-induced deterioration. Begin by rinsing finds thoroughly with fresh water and removing debris using soft-bristled brushes or wooden tools to avoid scratching. After cleaning, dry items completely using lint-free cloths and apply protective coatings appropriate for each metal type. Store artifacts in humidity-controlled containers with silica gel packets. Professional conservation methods offer additional techniques for preserving significant discoveries.
Key Takeaways
- Rinse beach finds immediately with fresh water to remove salt and sand, using a soft brush to prevent surface damage.
- Use controlled desalination through multiple distilled water baths to remove harmful chlorides from metal artifacts.
- Apply appropriate cleaning solutions based on metal type – soapy water for coins, diluted vinegar for iron objects.
- Thoroughly dry finds using microfiber cloths and fans, then apply protective coatings like wax or lacquer.
- Store cleaned items in humidity-controlled containers with silica gel packs, away from sunlight and chemical vapors.
Essential Field Cleaning Tips for Beach Discoveries
When discovering metal objects on the beach, proper field cleaning techniques are crucial for preserving both the artifact’s integrity and its historical value.
You’ll want to begin by using a soft-bristled brush to gently remove loose sand and debris, being careful not to damage delicate surfaces. Rather than dry brushing, rinse your finds with fresh water to dislodge abrasive particles, especially for coins or fragile items. Document the location of your finds through photos or notes to maintain their historical significance.
For stubborn mud deposits, utilize your fingernails, toothpicks, or small soft sticks, avoiding any scratching of the metal surface. Keep protective eyewear nearby when cleaning your finds to prevent sand or debris from getting in your eyes. These preservation techniques help protect your discoveries during transport.
Once cleaned, wrap your finds in soft cloth or paper envelopes instead of plastic bags to prevent moisture accumulation and additional corrosion. This methodical approach guarantees your beach finds remain stable until you can perform more thorough cleaning at home.
Salt Water Effects on Metal Artifacts
Although salt water initially appears harmless to metal artifacts, its electrochemical properties trigger severe deterioration through galvanic corrosion and electrolysis.
Seawater’s deceptively gentle appearance masks its corrosive power, unleashing devastating electrochemical reactions that destroy precious metal artifacts.
When you recover metal objects from marine environments, salt crystallization effects begin immediately as chloride ions penetrate microscopic pores in the metal’s structure. These chloride corrosion mechanisms create active cells that continuously degrade your finds, even after drying. The standard desalination process through alkaline solution soaking helps remove destructive chlorides but can take years to complete.
You’ll notice black crusts forming on the surface, masking extensive internal decay. As moisture evaporates, salt crystals expand within the metal’s microstructure, causing physical damage and flaking. Professional conservators often use X-radiography to assess the full extent of internal deterioration.
The process accelerates when oxygen exposure combines with residual salts, converting stable metals into fragile, powdery residues. If you don’t remove these destructive chlorides through proper desalination, your artifacts will continue deteriorating, regardless of storage conditions.
Safe Cleaning Methods for Beach Coins
When cleaning beach-found coins, you’ll need to first assess salt contamination levels by examining surface pitting, verdigris formation, and existing corrosion patterns.
To mitigate saltwater damage, you must implement a systematic cleaning protocol combining gentle water rinses, controlled soaking periods, and targeted mechanical cleaning with non-abrasive tools specific to each coin’s metallic composition. Improper cleaning methods can permanently damage or destroy valuable finds. Using soapy water solutions provides effective cleaning for medium-aged coins without causing surface damage.
After cleaning, you’ll require appropriate preservation measures, including thorough drying, application of protective waxes for copper specimens, and storage in humidity-controlled environments to prevent further deterioration.
Initial Saltwater Damage Assessment
Three critical factors determine your initial assessment of saltwater damage on beach-found coins: metal composition, physical condition, and corrosion patterns.
For metallurgy insights, examine your find under magnification to identify the base metal – gold coins resist corrosion while silver and copper pieces show significant deterioration. Check for telltale signs like black tarnish on silver or greenish patina on copper alloys. Coins enclosed in mint boxes tend to show better preservation against saltwater effects. Low water temperatures slow chemical reactions and help minimize environmental damage.
You’ll need to evaluate physical damage from sand abrasion, particularly on specimens found in shallow waters. Document edge wear, size reduction, and surface pitting before attempting any cleaning.
For corrosion prevention, immediately note the depth and location where you’ve recovered the coin, as these factors influence exposure severity and dictate your preservation strategy.
This systematic assessment guarantees you’ll make informed decisions about cleaning methods.
Gentle Multi-Stage Cleaning Process
Since beach-found coins require delicate handling, a systematic multi-stage cleaning process maximizes preservation while removing harmful contaminants.
You’ll need to employ sequential treatments that progress from least to most intensive, always maintaining control over the cleaning intensity.
- Begin with a distilled water soak to dissolve salt deposits, followed by gentle scrubbing with a soft-bristled brush.
- Apply hydrogen peroxide carefully to copper coins showing good detail, monitoring the bubbling action.
- Conduct extended olive oil or mineral oil soaks to soften stubborn corrosion, particularly effective for copper specimens.
- Finish with protective coatings like microcrystalline wax to seal against future degradation.
This methodical approach preserves numismatic value while effectively removing harmful beach residues.
Remember to document your progress and test methods on less valuable specimens first. For low-value silver pieces, consider using E-Zest cleaner to improve their appearance.
Using a stainless steel media during the cleaning process can help remove stubborn debris without damaging the coins’ surfaces.
Long-Term Storage Solutions
After meticulously cleaning your beach-found coins, proper storage techniques become crucial for long-term preservation.
Start by placing each coin in individual Mylar 2×2 flips or inert plastic capsules, avoiding PVC-based materials that can damage your artifacts over time.
For ideal coin preservation techniques, store your collection in specialized double-protection boxes equipped with silica gel packs for artifact humidity control.
Maintain environmental conditions below 50% relative humidity and keep temperatures stable. You’ll want to position your storage containers away from sunlight and areas with chemical vapors, such as garages or kitchens.
Monitor your collection regularly, replacing desiccant packs as needed. Use wooden or plastic tools when handling coins to prevent scratches, and always verify coins are completely dry before sealing them in their protective enclosures.
Restoring Copper and Brass Maritime Finds

Maritime copper and brass artifacts require specialized restoration techniques due to their unique exposure to saltwater corrosion and mineral deposits.
Saltwater exposure creates unique challenges when restoring copper and brass artifacts, demanding specialized techniques to combat corrosion damage.
You’ll need to implement a systematic approach combining electrolytic reduction and chemical stabilization to effectively restore these finds while preserving their historical integrity.
- Begin with gentle cleaning using hot soapy water and microfiber cloths, avoiding abrasive materials that could damage the surface.
- Apply electrolytic reduction by submerging the artifact in an electrolytic bath, monitoring hydrogen evolution to optimize chloride removal.
- Stabilize the metal through chemical treatment using alum and glycerin solutions, followed by thorough drying at 212°F.
- Protect the restored surface by applying specialized coatings like Incralac lacquer or microcrystalline wax after degreasing with acetone.
Handle your finds with gloves throughout the process to prevent contamination from skin oils and salts.
Treating Iron Objects Found in Sandy Environments
Iron objects discovered in sandy environments present unique preservation challenges due to their prolonged exposure to moisture, salts, and abrasive minerals.
You’ll need to carefully assess artifact fragility and the extent of iron corrosion before beginning any treatment process.
Start with gentle mechanical cleaning using soft wire brushes or bronze wool to remove loose deposits.
For stubborn rust, you can apply diluted white vinegar or lemon juice in controlled 5-minute soaks, followed by neutralization in a 5% baking soda solution.
Always test chemicals on a small area first.
After cleaning, thoroughly dry your finds and apply protective coatings like microcrystalline wax or specialized rust inhibitors.
Store artifacts in low-humidity conditions with desiccants to prevent renewed corrosion.
Monitor regularly for any signs of fresh rust formation.
Specialized Care for Beach Jewelry

When treating beach-found jewelry, you’ll need to first address salt removal through a controlled desalination process using distilled water baths changed at 24-hour intervals until chloride levels stabilize.
You must exercise particular caution with mixed-metal pieces, as galvanic corrosion can occur between different metals in the presence of residual salts.
For ideal preservation, you should document the initial condition, implement appropriate cleaning protocols based on metal composition, and maintain stable environmental conditions during the treatment process.
Salt Removal Techniques
Three critical salt removal techniques are vital for preserving beach-found jewelry from corrosive damage. To combat saltwater corrosion and guarantee proper jewelry preservation, you’ll need to implement immediate freshwater rinsing, mechanical cleaning, and protective treatments.
Each method targets specific aspects of salt removal while safeguarding your valuable finds.
- Start with an immediate freshwater rinse using distilled water to halt chloride-induced degradation.
- Deploy mechanical cleaning using a soft-bristled brush to remove embedded salt crystals from crevices and joints.
- Apply pH-neutral solutions to dissolve stubborn salt deposits without damaging metal surfaces.
- Finish with anti-tarnish protective coating to create a moisture barrier against future oxidation.
This systematic approach prevents long-term deterioration while maintaining the integrity of your beach-found treasures.
Mixed Metal Jewelry Care
Mixed metal jewelry recovered from beach environments requires specialized care protocols to maintain its structural integrity and aesthetic appeal.
Begin jewelry cleaning with a gentle rinse in warm water and mild soap, using a soft brush to remove sand and salt deposits. You’ll need to dry pieces thoroughly to prevent corrosion.
For metal preservation, store your finds in anti-tarnish bags or containers with moisture absorbers like silica gel. Keep different metal types separated to prevent chemical reactions.
Don’t use harsh cleaning agents or excessive polishing, as these can damage plating or thin delicate components. After beach exposure, promptly clean your pieces to minimize damage from salt and sand.
Regular maintenance with appropriate metal-specific cloths and cleaners will help preserve your finds’ appearance and value while preventing long-term deterioration.
Tools and Supplies for Beach Find Preservation
Successful preservation of beach metal detecting finds requires an extensive toolkit of specialized equipment and supplies.
Exploring the best spots for deep sea treasure can lead to exciting discoveries, whether it’s coins from shipwrecks or long-lost artifacts. The right gear can significantly enhance your chances of unearthing valuable items hidden beneath the waves. Additionally, understanding the ocean currents and local histories can guide your search to the most promising locations.
A well-equipped toolkit with specialized preservation tools is essential for safeguarding valuable beach-found metal treasures from degradation.
You’ll need a thorough array of preservation products and accessory tools to protect your discoveries from corrosion and deterioration. Proper handling starts with immediate freshwater rinsing and continues through long-term storage solutions.
- Deploy serrated-edge shovels and ergonomic scoops for efficient extraction while minimizing damage to finds.
- Apply environmentally friendly de-corroders and mild detergents using soft nylon brushes for initial cleaning.
- Create protective barriers with specialized preservation wax and anti-corrosion sprays.
- Utilize magnifiers and rare earth magnets for detailed inspection and sorting while maintaining organized storage in acid-free containers.
Choose waterproof equipment capable of handling high mineralization, and always carry protective gear for safe handling of potentially hazardous objects.
Proper Drying and Initial Treatment Techniques
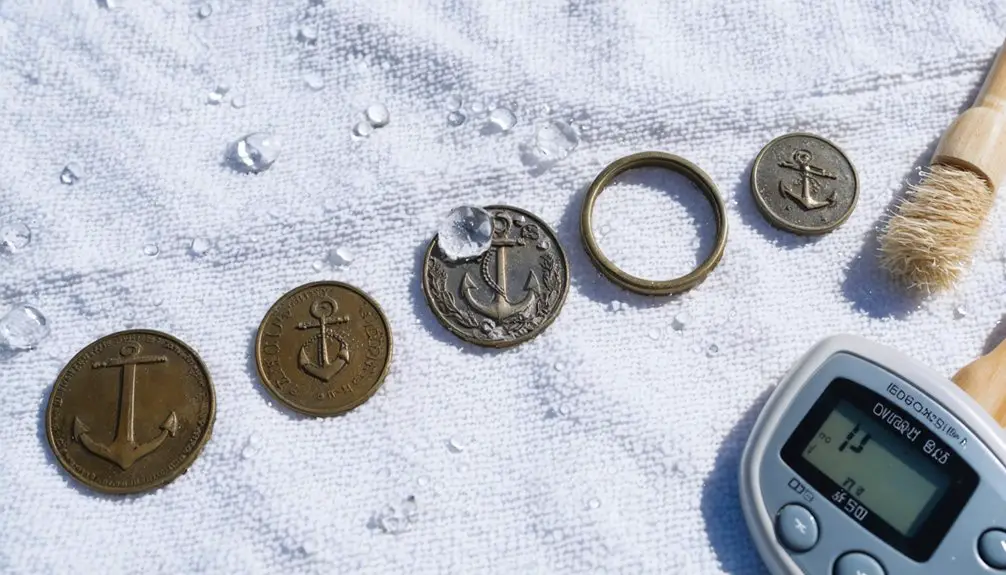
You’ll need to systematically remove salt deposits through controlled soaking and gentle brushing before implementing your chosen drying method, whether through ambient air circulation or dehumidification equipment.
To prevent flash rust formation during the drying process, maintain consistent environmental conditions while positioning your finds on elevated racks that maximize airflow exposure to all surfaces.
Your initial treatment protocol must incorporate proper temperature monitoring and relative humidity control to guarantee ideal preservation of the metal’s structural integrity during the critical drying phase.
Salt Removal Process Steps
When treating metal detecting finds from salt-contaminated environments, implementing a systematic salt removal process is critical for preserving the artifact’s integrity.
Salt removal techniques must be executed promptly to prevent ongoing corrosion and deterioration of your valuable discoveries. You’ll need to follow a precise methodology to guarantee effective preservation of your finds.
- Immerse your artifact in fresh water immediately after discovery, avoiding mechanical scrubbing that could damage delicate surfaces.
- Execute controlled electrolysis by placing items on aluminum foil in heated water, monitoring the reaction closely.
- Apply targeted chemical treatments based on specific metal composition, using mild solutions like hydrogen peroxide for silver items.
- Implement thorough fresh water rinsing to eliminate all treatment residues before initiating the drying process.
Air Drying Vs Dehumidifying
Following salt removal procedures, proper drying becomes the next critical phase in artifact preservation.
You’ll need to choose between two primary drying techniques: natural air drying or dehumidification. Air drying requires placing your finds on a clean, absorbent surface in a shaded, ventilated area, which can take several hours to days but reduces cracking risks in delicate pieces.
Dehumidification offers faster results by maintaining humidity levels below 50%, ideal for bulk processing.
Your choice of preservation methods should depend on the metal type. Iron and steel artifacts benefit from dehumidification’s controlled environment to prevent flash rust, while noble metals like gold and silver tolerate air drying better.
For best results, avoid stacking items during either process, and consider applying protective coatings immediately after drying to guarantee long-term preservation.
Preventing Flash Rust Formation
To prevent flash rust formation on metal detecting finds, immediate and methodical post-recovery treatment proves essential for long-term preservation.
Your initial actions will determine whether your finds maintain their integrity or succumb to rapid oxidation. Effective flash rust prevention requires swift surface moisture removal followed by targeted stabilization techniques.
- Remove surface contaminants using fresh water rinses, then immediately pat dry with lint-free microfiber cloths.
- Apply controlled airflow in a ventilated space using fans or cool-setting heat guns for thorough drying.
- Treat dried surfaces promptly with corrosion inhibitors like mineral oil or Renaissance wax.
- Store items in airtight containers with silica gel packets, avoiding environments that trap moisture.
Test all treatments on small areas first, particularly with precious metals or delicate artifacts requiring specialized care.
Long-Term Storage Solutions for Coastal Artifacts
Since coastal artifacts are particularly vulnerable to salt-induced corrosion, implementing proper long-term storage solutions becomes crucial for their preservation.
You’ll need to establish controlled storage environments that maintain stable temperature and humidity levels while protecting your finds from damaging environmental factors.
Start by organizing your artifacts through proper artifact classification, using archival-quality, acid-free materials for smaller items.
Careful organization and archival-grade materials form the foundation of proper artifact preservation and classification systems.
Install non-off-gassing cabinets and adjustable shelving systems to accommodate your growing collection while guaranteeing adequate protection from dust, light, and pests.
You’ll maximize your storage capacity by implementing high-density mobile shelving, which helps optimize available space without compromising accessibility.
For extensive protection, equip your storage facility with continuous monitoring systems, including video surveillance and climate control mechanisms.
This systematic approach guarantees your coastal finds remain preserved for years to come.
Professional Conservation Considerations
Professional metal detecting conservation demands specialized expertise and methodical approaches to guarantee artifacts retain their historical and monetary value.
When you’re dealing with significant finds, conservation ethics require consulting specialists like Finds Liaison Officers before attempting any treatment.
- You’ll need professional assessment for complex artifacts, particularly those containing multiple metal types or showing active corrosion.
- Consider anoxic conservation methods using specialized barrier films and oxygen scavengers for valuable pieces requiring long-term preservation.
- Let experts handle chemical treatments for tarnished silver or corroded copper alloys to prevent irreversible damage.
- Submit historically significant items to professional conservators who can properly document, clean, and stabilize finds using advanced techniques like Paraloid B72 coatings.
Your freedom to clean and preserve finds shouldn’t compromise their integrity – when in doubt, seek professional guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Should I Wait Before Cleaning Items Found in Wet Sand?
You’ll need 24-48 hours minimum drying time before applying cleaning methods to wet sand finds. For ideal drying techniques with delicate metals, extend this period to several days.
Can Salt-Damaged Artifacts Be Restored to Their Original Condition?
You can’t fully restore salt-damaged artifacts to original condition despite restoration techniques. While artifact preservation methods can stabilize and improve their state, some surface alterations and material loss remain permanent.
What Temperature Should I Store My Beach Finds At?
You’ll want to maintain storage conditions between 15-25°C (59-77°F), avoiding temperature fluctuations. Keep your finds in a stable indoor environment away from heaters, air conditioners, and direct sunlight.
Are Metal Detectors With Higher Frequencies Better for Beach Hunting?
As waves lap at your feet, high frequencies aren’t always your best choice. You’ll face significant interference from mineralization. Instead, opt for multi-frequency detectors that’ll give you versatility and depth for beach hunting.
How Can I Identify if a Beach Find Has Historical Significance?
You’ll need to examine manufacturing marks, analyze historical context through provenance research, and evaluate the artifact’s material composition against known typologies of regional maritime or coastal artifacts.
References
- https://detectorpower.com/blogs/metal-detectors/how-to-clean-metal-detector-finds
- https://www.metaldetector.com/blogs/new_blog/care-preservation-of-relics-found-with-metal-detectors
- https://www.metaldetectingforum.co.uk/viewtopic.php?t=30112
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EPvy059r7qQ
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5HNkEKrcVWA
- https://treasurecoastmetaldetectors.com/blogs/news-1/how-to-identify-and-clean-your-metal-detecting-finds
- https://www.minelab.com/blog/article/how-to-clean-and-preserve-your-finds
- http://www.cawreckdivers.org/Preservation.htm
- https://www.clemson.edu/centers-institutes/conservation/equipment/compressed_fluids.html
- https://www.history.navy.mil/research/underwater-archaeology/conservation-and-curation/ua-conservation-heritage.html



